Have you ever considered why certain textiles shame others when they feel more plush and comfortable? What explains why some textiles prove more durable together, maintaining their long life? Yarn twisting determines the composite strength and comfort level of the resulting fabric.
Both fabric functionality and design outcome depend heavily upon how freely yarns twist and the directionality of their twists. Knitters and crocheters will make better project choices if they comprehend yarn twists alongside textile enthusiasts. Continue reading to find out the substantial impact that this subtle attribute produces.
An Overview of Yarn Twist
Yarn twist expresses the degree of tightness at which fibres combine during the spinning process. Textile appearance and performance rely on the specific twists applied because different twist types generate distinct textures.
High Twist
Technicians spin the fibres together more closely during high-twist yarn production to produce their characteristic tight-twist structure. Manufacturing tightly twisted yarn produces a smooth and tough material for strong fabrics like denim.
The high twists in yarn generate clear-cut details because they resist pilling better. Because tightly twisted fibres generate high twists, these yarns often feel stiff, affecting their drape capabilities.
Low Twist
Loose twisting in yarn lets fibres maintain greater distance throughout their structure. Low-twist fibres create a fabric with superior flexibility, softness, and improved draping abilities, suitable for clothing, upholstery, and other comfort-oriented designs. These fabrics get damaged more quickly because loose-shaped fibres in a low-twist yarn readily grab against surfaces, thus falling out easily.
Medium Twist
Most yarn types exhibit properties between low and high twist levels. Fabrics created from medium twisted yarn must satisfy both comfort through softness and durability requirements. Combining fibre selection with controlled yarn thickness and specific twisting speed and tension allows producers to create twist levels appropriate for various applications.
How Yarn Twist Impacts Appearance and Texture

A finished textile demonstrates differing visual and tactile characteristics based on how its constituent yarn is twisted. Fine textures form when yarn twists tightly, producing dense fabrics with hardness and smoothness, but loosely twisted yarns produce flexible fabrics that display porosity and fuzziness on their surfaces.
- Clothing and Comfort: Loosely twisted yarn creates garments with greater comfort and fluid motion, making them perfect for summer wear. These include flowing dresses alongside comfortable sweaters.
- Durability and Structure: Tightly twisted yarns are the basis for durable and structured fashion items, including denim jeans, canvas jackets, and corduroy pants.
- Dye Absorption: Dyes attach to the increased surface area of loosely twisted yarns, creating bold, saturated colours. Yarn twists with higher tension conceal more fibres, affecting colour with lighter and patchier results.
The twist demonstrates functional purposes as well as serving visual functions. Yarns with loose twists show increased pilling under prolonged use yet maintain better air circulation until their structure becomes solidified due to tight twisting for durability.
Yarn Twist and Strength: Finding the Right Balance
Twisting yarns increases strength, durability, and elasticity, but twisting beyond the optimal point decreases these qualities. Discovering the ideal twist strength for yarn variety and fabric purpose remains fundamental.
Moderate Twist
Knitting projects benefit from most yarns which maintain strong structural integrity at a twist ratio between three and five turns per inch. The fibers remain firmly bound together by a twist which maintains maximum yarn integrity.
Over-Twisting
Twining a yarn past its optimal twist lets it fold back on its path and generates snarls and kinks, subsequently damaging the yarn. The presence of defects makes yarn harder to work with during knitting or weaving because they force stress points, which lead to breakage when worn under tension. When natural materials such as cotton receive excessive twisting during processing, they become matted and transform into large ropelike fibres.
Determining the perfect yarn twist requires balancing the attributes of strength and durability against softness, stretch, and how well the yarn hangs.
Choosing Yarn Twists for Specific Fabrics
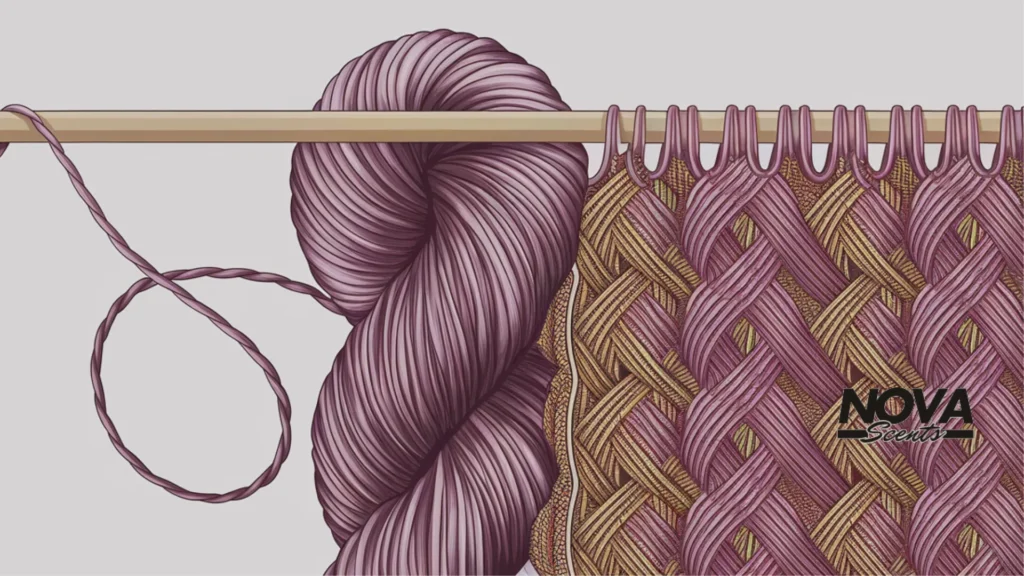

When choosing a yarn for your textile project, consider how many twists you want based on the intended use:
- Soft, Drape-Friendly Fabrics: Upholstery, bedding, and clothing find their best match in loose twists because they result in flexible and comfortable structures.
- Durable, High-Strength Fabrics: Outdoor gear, industrial textiles, and furniture fabrics display better longevity when constructed with tightly twisted yarns.
- Balanced Medium Twist: Medium twists provide versatile textile solutions because they combine strong durability together with softness.
The texture of a fabric surface varies with changes in the twist amount. Textile surfaces become smooth with high twists but demonstrate a rustic texture at lower twist levels.
Experimenting with Yarn Twists in Textile Design
Designers who change yarn twist patterns can produce distinctive textures in textile items. Yarn twisting techniques enable designers to develop fabrics from identical fibre materials with diverse characteristics.
Twist Variations
- High-twist (70-80 turns per inch): Produces a dense, durable yarn for rugs, placemats, and upholstery.
- Medium-twist (50-70 turns per inch): A versatile, all-purpose yarn suitable for apparel and accessories.
- Low-twist (30-50 turns per inch): Low-twist yarn performs best when used to create easy-care drapery fabrics that flow beautifully next to shawls and loungewear.
Consumer creativity flourishes with varied yarn twist types in materials construction. When you combine high-twist wool with low-twist silk, you make a yarn blend that provides both warmth and a shiny matte finish. Combining different yarn twists creates rich depth, appealing texture, and visual complexity in design work.
Conclusion
Textile aesthetics and functionality heavily rely on yarn twist count and sequence direction. When you select fabric, yarn, or finished clothing for your project, examine the yarn twist to understand how it affects drape durability and texture.
When you focus on these details of textile products, you begin to understand the expertise in science and craftsmanship needed to create such fabrics. Choosing the suitable yarn twist allows manufacturers to create materials that demonstrate optimal functionality, aesthetic appeal, and durability.
Olivia Hart is a business analyst passionate about entrepreneurship, providing insights and strategies for startups and established companies alike.